The Western music system uses 12 notes within each octave. On the keyboard these are the 7 white keys and 5 black keys.
When all twelve notes within the octave are placed in ascending (or descending) order they form the chromatic scale
('chromatic' means 'colour').
The chromatic scale is called a symmetric scale, because all the notes in the scale are
spaced at equal (semitone) intervals.
Audio 8.3
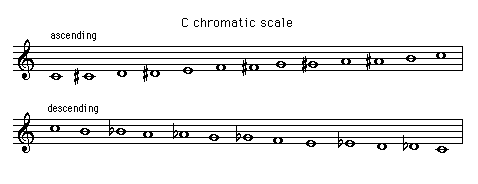
When ascending the chromatic scale (or a chromatic passage) is written with sharp signs.
When descending the chromatic scale (or a chromatic passage) is written with flat signs.